Metabolism can roughly be defined as the chemistry that turns food into life, and therefore insulin and leptin are both critical to health and disease. Insulin and leptin work together to control the quality of your metabolism, and, to a significant extent, your rate of metabolism.
By acquiring a better understanding of how leptin and its receptor interact, researchers now believe they will be able to find new treatments for obesity and other metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes, as well as inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis.
According to recent research published in the journal Molecular Cell,1 the leptin receptor has two hinged legs that swivel until they come in contact with leptin.
Once leptin attaches to the receptor, these legs stop swiveling and become rigid, thereby sending a signal to an enzyme called Janus kinase,2 which has the ability to bind inflammatory cytokines. It is believed that inhibiting the Janus kinases might help improve inflammatory and metabolic disorders.
The fact that the primary focus is on developing drug therapies to “fix” leptin resistance is understandable. That’s the only way the medical industry can make money. However, the way to correct leptin resistance has nothing to do with drugs, and everything to do with diet. But first…
What Exactly is Leptin?
Leptin is a very powerful and influential hormone produced by your fat cells. Your fat, by way of leptin, tells your brain whether you should be hungry, eat and make more fat, whether you should reproduce, or (partly by controlling insulin) whether to engage in maintenance and repair. In short, leptin is the way that your fat stores speak to your brain to let your brain know how much energy is available and, very importantly, what to do with it.
Therefore, leptin may be on top of the food chain in metabolic importance and relevance to disease.
If your leptin signaling is working properly, when your fat stores are “full,” this extra fat will cause a surge in your leptin level, which signals your brain to stop feeling hungry, to stop eating, to stop storing fat and to start burning some extra fat off.
Controlling hunger is a major (though not the only) way that leptin controls energy storage. Hunger is a very powerful, ancient, and deep-seated drive that, if stimulated long enough, will make you eat and store more energy. The only way to eat less in the long-term is to not be hungry, and the only way to do this is to control the hormones that regulate hunger, the primary one being leptin.
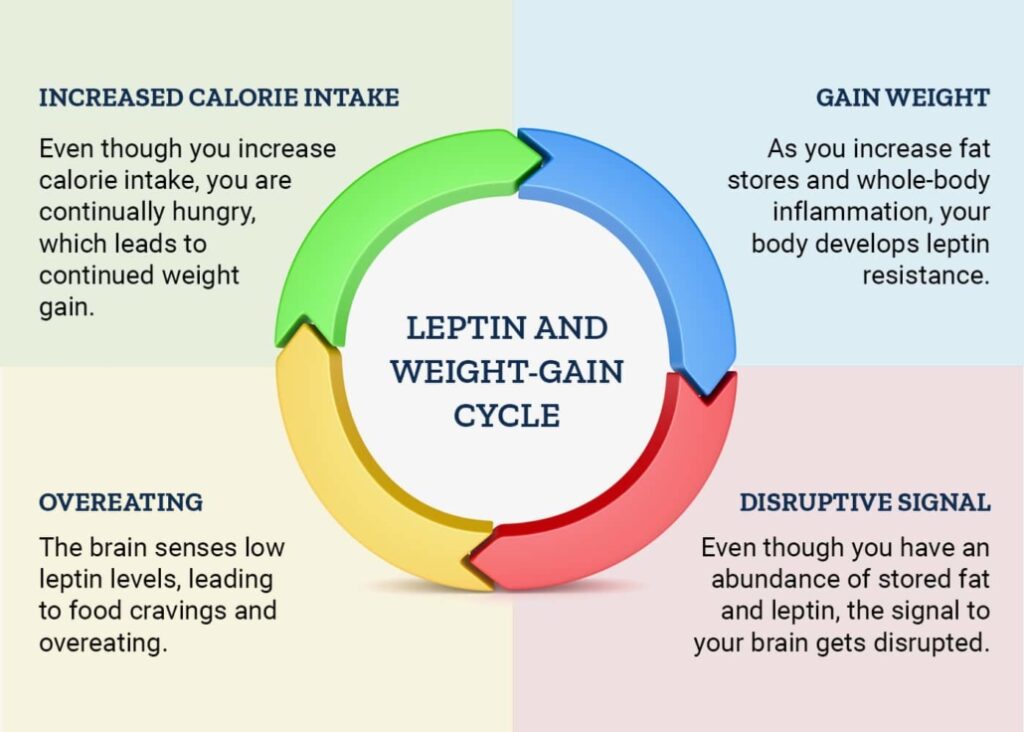
How Do You Become Leptin Resistant?5 rules of leptin diet
You become leptin-resistant by the same general mechanism that you become insulin-resistant – by continuous overexposure to high levels of the hormone. If you eat a diet that is high in sugar (particularly fructose), grains, and processed foods – the same type of diet that will also increase inflammation in your body – as the sugar gets metabolized in your fat cells, the fat releases surges in leptin.
Over time, if your body is exposed to too much leptin, it will become resistant, just as your body can become resistant to insulin.
The only known way to reestablish proper leptin (and insulin) signaling is to prevent those surges, and the only known way to do that is via diet. As such, diet can have a more profound effect on your health than any other known modality of medical treatment.
A strategic whole food diet, as detailed in my free nutrition plan, that emphasizes good fats and avoids blood sugar spikes coupled with targeted supplements will enhance insulin and leptin sensitivity so that your brain can once again hear the feedback signals from these hormones.
So to summarize: Insulin and leptin resistance are core factors in obesity, which in turn is a risk factor for cancer and may boost tumor growth. But the answer lies not in a pill. To reverse insulin and leptin resistance:
Avoid, sugar, fructose, grains, and processed foods
Eat a healthful diet of whole foods, ideally organic, and replace the grain carbs with:
No-to-low sugar and grain carbs
Low-to-moderate amount of protein
As much highly quality healthful fat as you want (saturated and monosaturated). Most people need upwards of 50-70 percent fats in their diet for optimal health. Good sources include coconut and coconut oil, avocados, butter, nuts, and animal fats. Also take a high-quality source of animal-based omega-3 fat, such as krill oil
Similarly, while researchers investigate the pharmaceutical avenues to convert white fat cells to brown in an effort to reduce the potential for cancer growth, other research has already shown that this can likely be achieved through exercise.
As I’ve said before, about 80 percent of the health benefits you reap from a healthy lifestyle comes from your diet, and the remaining 20 percent from exercise – but it’s a very important 20 percent, as it acts in tandem with and boosts the benefits derived from a proper diet. For maximum benefits, you’ll want to make sure to include high-intensity interval training, which is at the heart of my Peak Fitness program.



